ALIGNVLM: Bridging Vision and Language Latent Spaces for Multimodal Document Understanding
Abstract
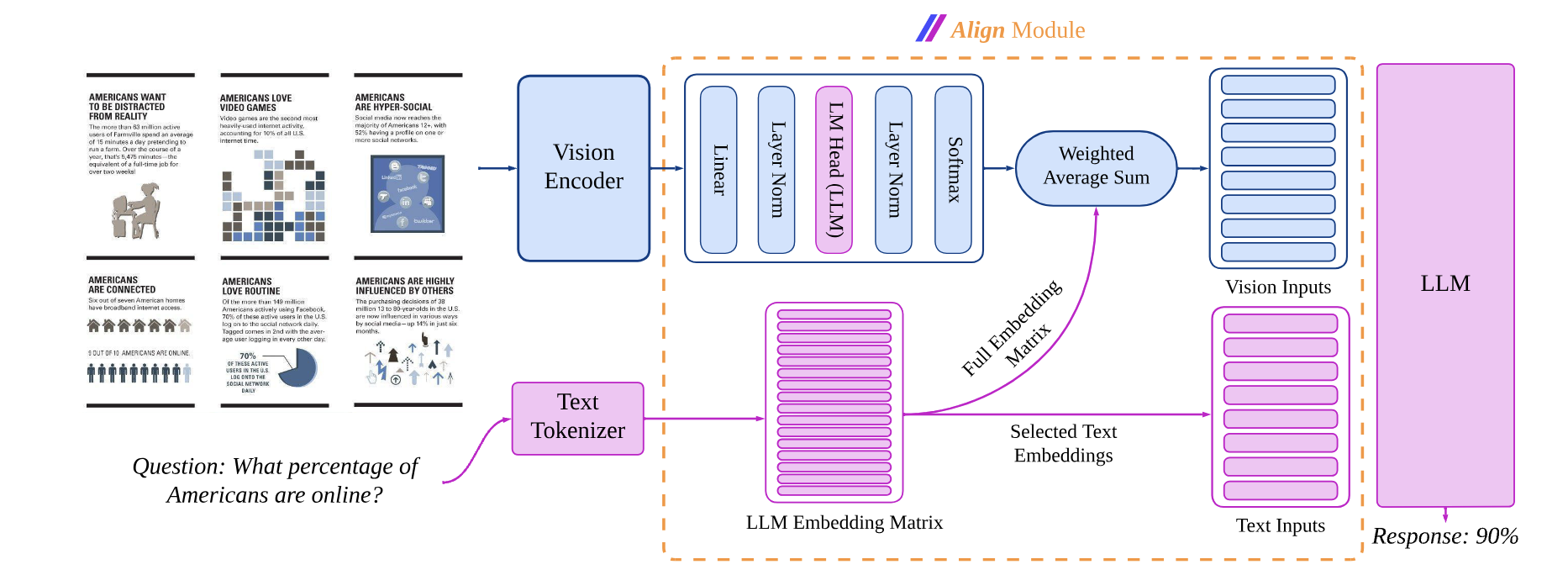
Aligning visual features with language embeddings is a key challenge in vision-language models (VLMs). The performance of such models hinges on having a good connector that maps visual features generated by a vision encoder to a shared embedding space with the LLM while preserving semantic similarity. Existing connectors, such as multilayer perceptrons (MLPs), lack inductive bias to constrain visual features within the linguistic structure of the LLM's embedding space, making them data-hungry and prone to misalignment between the modalities.
In this work, we propose a novel vision-text alignment method, ALIGNVLM, that maps visual features to a weighted average of LLM text embeddings. Our approach leverages the linguistic priors encoded by the LLM to ensure that visual features are mapped to regions of the space that the LLM can effectively interpret. ALIGNVLM is particularly effective for document understanding tasks, where visual and textual modalities are highly correlated.
Our extensive experiments show that ALIGNVLM achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to prior alignment methods, with larger gains on document understanding and under low-resource setups. We provide further analysis demonstrating its efficiency and robustness to noise. Our experimental results show that ALIGN improves performance on various document understanding tasks, outperforming prior connector methods, with especially large gains in low-data regimes.
Main Contributions:
- We propose a novel connector, ALIGN, to bridge the representation gap between vision and text modalities.
- We introduce a family of Vision-Language Models, ALIGNVLM, that achieves state-of-the-art performance on multimodal document understanding tasks by leveraging ALIGN.
- We conduct extensive experiments demonstrating the robustness and effectiveness of ALIGN across different LLM sizes, vision encoders, and training data setups.
Main Results on General Document Benchmarks
We compare ALIGNVLM (ours) with state-of-the-art (SOTA) open and closed-source instructed models. ALIGNVLM models outperform all Base VLM models trained in the same data regime and perform competitively across document benchmarks even compared with SOTA models.
| Model | DocVQA VAL |
InfoVQA VAL |
DeepForm TEST |
KLC TEST |
WTQ TEST |
TabFact TEST |
ChartQA TEST |
TextVQA VAL |
TableVQA TEST |
Avg. Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closed-Source VLMs (Opaque Training Data) |
||||||||||
| Claude-3.5 Sonnet | 88.48 | 59.05 | 31.41 | 24.82 | 47.13 | 53.48 | 51.84 | 71.42 | 81.27 | 56.54 |
| GeminiPro-1.5 | 91.23 | 73.94 | 32.16 | 24.07 | 50.29 | 71.22 | 34.68 | 68.16 | 80.43 | 58.46 |
| GPT-4o 20240806 | 92.80 | 66.37 | 38.39 | 29.92 | 46.63 | 81.10 | 85.70 | 70.46 | 72.87 | 64.91 |
| Open-Source Instruct VLMs (Semi-Opaque Training Data) |
||||||||||
| Janus-1.3B | 30.15 | 17.09 | 0.62 | 15.06 | 9.30 | 51.34 | 57.20 | 51.97 | 18.67 | 27.93 |
| Qwen2-VL-2B | 89.16 | 64.11 | 32.38 | 25.18 | 38.20 | 57.21 | 73.40 | 79.90 | 43.07 | 55.84 |
| Qwen2.5-VL-3B | 93.00 | 75.83 | 32.84 | 24.82 | 53.46 | 71.16 | 83.91 | 79.29 | 71.66 | 65.10 |
| InternVL-2.5-2B | 87.70 | 61.85 | 13.14 | 16.58 | 36.33 | 57.26 | 74.96 | 76.85 | 42.20 | 51.87 |
| InternVL-3-2B | 87.33 | 66.99 | 37.90 | 29.79 | 39.44 | 59.91 | 75.32 | 78.69 | 43.46 | 57.64 |
| DeepSeek-VL2-Tiny-3.4B | 88.57 | 63.88 | 25.11 | 19.04 | 35.07 | 52.15 | 80.92 | 80.48 | 56.30 | 55.72 |
| Phi3.5-Vision-4B | 86.00 | 56.20 | 10.47 | 7.49 | 17.18 | 30.43 | 82.16 | 73.12 | 70.70 | 48.19 |
| Qwen2-VL-7B | 93.83 | 76.12 | 34.55 | 23.37 | 52.52 | 74.68 | 83.16 | 84.48 | 53.97 | 64.08 |
| Qwen2.5-VL-7B | 94.88 | 82.49 | 42.21 | 24.26 | 61.96 | 78.56 | 86.00 | 85.35 | 76.10 | 70.20 |
| LLaVA-NeXT-7B | 63.51 | 30.90 | 1.30 | 5.35 | 20.06 | 52.83 | 52.12 | 65.10 | 32.87 | 36.00 |
| DocOwl1.5-8B | 80.73 | 49.94 | 68.84 | 37.99 | 38.87 | 79.67 | 68.56 | 68.91 | 52.60 | 60.68 |
| InternVL-2.5-8B | 91.98 | 75.36 | 34.55 | 22.31 | 50.33 | 74.75 | 82.84 | 79.00 | 52.10 | 62.58 |
| InternVL-3-8B | 91.99 | 73.90 | 51.24 | 36.41 | 53.60 | 72.27 | 85.60 | 82.41 | 53.26 | 66.74 |
| Fuyu-8B | 48.97 | 23.09 | 4.78 | 6.63 | 14.55 | 47.91 | 44.36 | 46.02 | 15.49 | 22.97 |
| Ovis-1.6-Gemma2-9B | 88.84 | 73.97 | 45.16 | 23.91 | 50.72 | 76.66 | 81.40 | 77.73 | 48.33 | 62.96 |
| Llama3.2-11B | 82.71 | 36.62 | 1.78 | 3.47 | 23.03 | 58.33 | 23.80 | 54.28 | 22.40 | 34.04 |
| Pixtral-12B | 87.67 | 49.45 | 27.37 | 24.07 | 45.18 | 73.53 | 71.80 | 76.09 | 67.13 | 58.03 |
| Document Understanding Instructed Models (Instruction Tuned on BigDocs-7.5M + DocDownStream) |
||||||||||
| Qwen2-VL-2B (base+) | 57.23 | 31.88 | 49.31 | 34.39 | 31.61 | 64.75 | 68.60 | 61.01 | 47.53 | 49.59 |
| ALIGNVLM-Llama-3.2-1B (ours) | 72.42 | 38.16 | 60.47 | 33.71 | 28.66 | 71.31 | 65.44 | 48.81 | 50.29 | 52.14 |
| ALIGNVLM-Llama-3.2-3B (ours) | 79.63 | 44.53 | 63.49 | 35.25 | 38.59 | 78.51 | 71.88 | 57.38 | 60.10 | 58.81 |
| DocOwl1.5-8B (base+) | 78.70 | 47.62 | 64.39 | 36.93 | 35.69 | 72.65 | 65.80 | 67.30 | 49.03 | 57.56 |
| Llama3.2-11B (base+) | 78.99 | 44.27 | 67.05 | 37.22 | 40.18 | 78.04 | 71.40 | 68.46 | 56.73 | 60.26 |
| ALIGNVLM-Llama-3.1-8B (ours) | 81.18 | 53.75 | 63.25 | 35.50 | 45.31 | 83.04 | 75.00 | 64.60 | 64.33 | 62.88 |